As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to expand, choosing the right connectivity option is critical for the success of IoT deployments. Among the various choices available, “4G Connectivity for IoT” has emerged as the most common and practical solution. Its balance of speed, coverage, and cost makes it a versatile option for a wide range of IoT applications. To fully understand the impact of connectivity, start by learning what IoT is.
While newer technologies like 5G and specialized options such as NB-IoT and LoRaWAN offer distinct advantages, 4G remains the go-to choice for many IoT projects due to its reliability and global reach. This article explores why 4G is the preferred connectivity for IoT, how it compares to other technologies, and where it fits into the evolving landscape of IoT connectivity.
Why 4G is the Most Common Connectivity for IoT

4G has established itself as the most widely used connectivity option in the IoT ecosystem due to its unique balance of speed, coverage, and cost-effectiveness. As IoT devices evolve and network infrastructures change, it’s crucial to choose the right carrier technology to maximize the benefits of 4G connectivity. With global reach and mature infrastructure, 4G offers reliable and stable connections, making it suitable for a broad range of IoT applications. Additionally, 4G’s capability to handle substantial data traffic with relatively low latency ensures that IoT devices can communicate effectively, whether deployed in urban centers or remote locations.
While 5G promises higher speeds and lower latency, its infrastructure is still being developed, and its coverage is limited compared to 4G. On the other hand, specialized technologies like NB-IoT and LoRaWAN excel in low-power, long-range applications but may lack the versatility and bandwidth needed for more data-intensive IoT applications.
The widespread adoption of 4G in IoT is driven by its ability to deliver consistent performance across diverse environments, making it a practical choice for both large-scale deployments and individual devices. Whether in smart cities, transportation, healthcare, or industrial automation, 4G’s adaptability ensures that IoT devices can operate efficiently, with robust connectivity.
Benefits of 4G for IoT Solutions
4G connectivity offers several significant benefits for IoT solutions, making it a preferred choice for many deployments.
Reliable and Stable Connections: 4G networks provide consistent and dependable connectivity, which is crucial for IoT devices that require continuous communication.
Global Coverage and Roaming Capabilities: With widespread 4G infrastructure, IoT devices can operate across various regions without connectivity issues, making it ideal for global deployments.
Low Latency and Sufficient Bandwidth: 4G supports low-latency communication, enabling real-time data transmission, essential for applications like telematics and remote monitoring.
Security Features: 4G networks come equipped with robust security protocols, ensuring that data transmitted by IoT devices remains protected against potential threats.
In summary, 4G’s reliability, coverage, and security make it an excellent choice for IoT applications, supporting a wide range of industries and use cases.
Comparing 4G with Other Connectivity Options
As IoT solutions continue to evolve, it’s essential to understand how 4G compares with other connectivity technologies to determine the best fit for specific applications. Explore the advantages of a technology-agnostic IoT approach to see how 4G can be part of a hybrid connectivity solution.
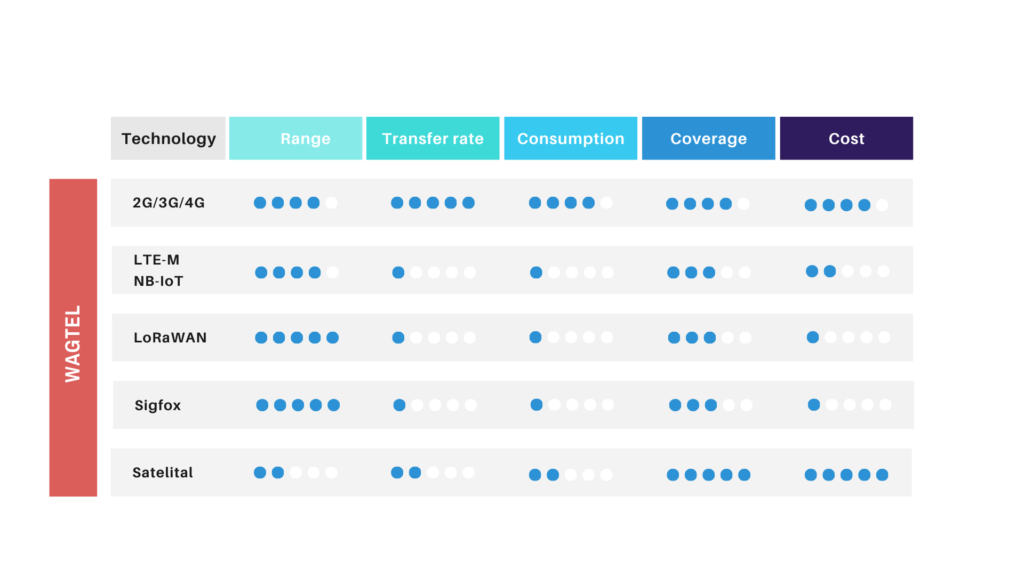
4G vs. 5G: While 5G offers higher speeds and lower latency, 4G remains the more practical choice for most IoT applications due to its mature infrastructure and broader coverage. Many IoT devices don’t require the extreme speed and ultra-low latency that 5G provides, making 4G a reliable and cost-effective option.
4G vs. NB-IoT: NB-IoT is designed for low-power, wide-area applications, such as remote monitoring and environmental sensing. It offers excellent coverage and battery life but lacks the bandwidth for data-heavy applications. 4G, however, provides sufficient bandwidth and speed for a broader range of IoT use cases while still supporting lower-power needs in many instances.
4G vs. LoRaWAN: LoRaWAN is another low-power option with long-range capabilities, particularly useful in rural and remote areas. However, it operates on unlicensed spectrum, which can lead to interference and reliability issues. In contrast, 4G operates on licensed spectrum, offering more stable and secure connections suitable for a wider variety of IoT applications, including those in urban areas where interference might be a concern.
In conclusion, while alternative connectivity options like 5G, NB-IoT, and LoRaWAN each have their strengths, 4G stands out for its versatility, reliability, and global reach. It’s the go-to solution for many IoT deployments that require a balance of coverage, speed, and cost.
Real-World Applications of 4G in IoT

4G connectivity is widely used across various industries, supporting a broad spectrum of IoT applications. In smart cities, 4G enables real-time data exchange for traffic management, environmental monitoring, and public safety systems. For more insights on how 4G enhances smart home technology, check out our article on cellular connectivity in smart homes. In transportation, 4G facilitates vehicle tracking, fleet management, and telematics, ensuring efficient and secure operations. Healthcare is another sector where 4G plays a crucial role, enabling remote patient monitoring and telemedicine services with reliable connectivity.
Additionally, industrial automation benefits from 4G’s robust connectivity, supporting remote control and monitoring of machinery in factories and other industrial settings.
By leveraging 4G, these industries can enhance operational efficiency, improve safety, and deliver better services, all while maintaining reliable and secure communication channels.
Future of 4G in the IoT Landscape
As IoT continues to evolve, 4G remains vital, even as 5G and advanced technologies gain traction. With the 2G and 3G network sunset approaching, 4G stands as a crucial option for IoT. Its integration with technologies like NB-IoT and LoRaWAN is likely, enabling efficient and cost-effective deployments, particularly where coverage, power consumption, and data transfer speed are key. As IoT grows, 4G will bridge the gap between existing infrastructure and next-gen networks.
Conclusion
4G remains a vital connectivity option for IoT deployments due to its reliability, global coverage, and cost-effectiveness. While newer technologies like 5G and specialized options like NB-IoT and LoRaWAN are making strides, 4G continues to offer the right balance for a wide range of IoT applications. Its ongoing relevance is assured as it integrates with emerging technologies to create hybrid solutions that address various connectivity needs. For those looking to deploy IoT solutions, 4G provides a robust and dependable foundation.
Explore how Wagtel’s IoT solutions can enhance your connectivity strategy and ensure your IoT deployments are future-proof. Reach out to us today to learn more about how we can support your IoT projects.






